
Information Technology Business Continuity Plan
The sustainability of an enterprise’s data resources has reached a level of importance that cannot be ignored. Business continuity and disaster recovery solutions are an integral consideration for modern-day businesses across the world, and with good reason. Organizational leaders who fail to implement a business continuity strategy are risking the health of their entire business, costing them customers, sales and even their reputation.
This guide will explain the essential components and steps to creating and implementing an effective information technology business continuity plan (IT BCP) tailored to your organization’s needs.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Business Continuity Plan?
- Why Is a Business Continuity Plan Important?
- Challenges of a Business Continuity Plan
- What Does a Business Continuity Plan Include?
- Steps to Create a Business Continuity Plan
- Plan Implementation
- Plan Testing
- Business Continuity in the Cloud
What Is a Business Continuity Plan?
A business continuity plan is a strategic document that outlines procedures and protocols to help continue business operations during unforeseen situations. It describes a framework used to determine a company’s vulnerability to internal and external threats, what would happen if certain disastrous scenarios actually materialized and how a company would respond to each possible scenario.
This framework aims to provide organizations with a plan to effectively respond to events threatening their ability to continue operations as usual. Part of your strategy should include a detailed set of procedures to retrieve the applications and data that would be lost in case a disaster occurs. This is called disaster recovery, and your managed IT support company will be responsible for this portion of the backup plan.

Why Is a Business Continuity Plan Important?
In today’s fast-paced business environment, having a BCP is more important than ever. It provides a structured approach to navigating unforeseen disruptions and crises. A BCP ensures operations can continue smoothly, even in the face of challenges like cyber threats, natural disasters or pandemics.
By integrating crisis management and business continuity strategies, businesses can serve customers during a crisis, reducing the chance of customers turning to competitors. These strategies reduce the amount of time a company is unable to operate. A BCP also details the actions to be followed to ensure the company’s financial stability, both prior to, during and after an emergency.
Challenges of a Business Continuity Plan
Navigating the waters of business continuity planning isn’t always smooth sailing. While essential, crafting an effective BCP comes with its fair share of challenges:
Complexity of Modern Businesses
Managing the complex IT infrastructures and interconnected systems of modern companies is a major challenge. Identifying and prioritizing important assets can be daunting, especially for organizations that have restricted resources.
Maintaining Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring the BCP aligns with industry standards and legal requirements requires attention to detail and continuous monitoring.
Dynamic Nature of Threats and Risks
Technology progresses quickly, resulting in the rise of new risks. Businesses must continuously update and adapt their BCPs to address evolving risks effectively. Testing the plan’s effectiveness against various scenarios is crucial but challenging.
Achieving Stakeholder Buy-In
Getting employees to participate actively in the development and implementation of BCP can be challenging. Securing buy-in and participation from stakeholders at all levels of the organization requires effective communication and leadership.
Securing Funding and Resources
Securing enough funding and resources for BCP projects can pose challenges, especially for small businesses operating on tight budgets. Securing support from decision-makers and allocating resources strategically are key to overcoming this challenge.
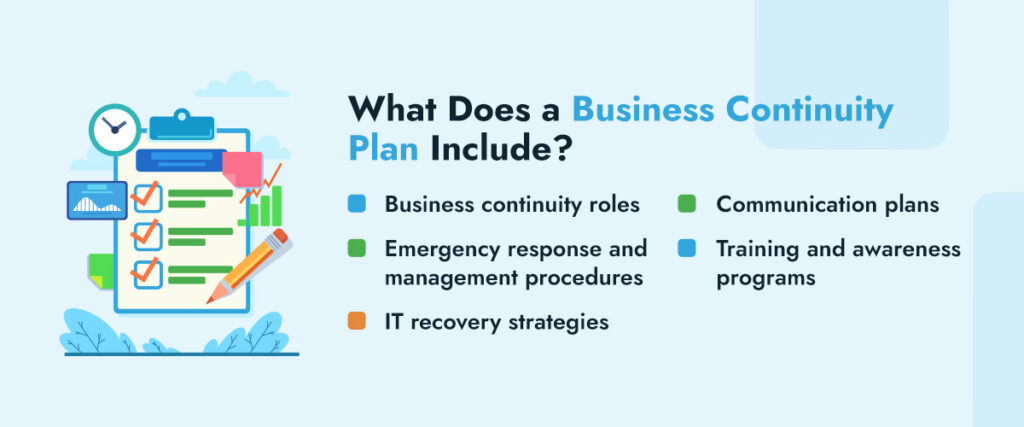
What Does a Business Continuity Plan Include?
Creating a business continuity plan to improve information security involves incorporating essential components to ensure comprehensive coverage and effective response strategies. A BCP should typically include the following:
- Business continuity roles: Assigning specific duties and obligations is vital for effective BCP implementation. This involves designating a BCP coordinator, crisis management team members and individuals in charge of communication, IT recovery and logistics.
- Emergency response and management procedures: Creating clear protocols for responding to emergencies is crucial in minimizing downtime and ensuring the safety of staff and stakeholders. This includes procedures for evacuations, medical emergencies and communication with external parties such as emergency responders and vendors.
- IT recovery strategies: Developing IT recovery strategies is crucial for restoring critical systems and minimizing disruption to business operations. These strategies include backup and recovery plans, redundant infrastructure, and procedures for restoring data and applications.
- Communication plans: During crises, effective communication is crucial to coordinating and sharing important information. Developing communication plans that outline protocols for internal and external communication channels helps maintain transparency and facilitate timely updates.
- Training and awareness programs: Training and awareness programs ensure employees know their roles and responsibilities during emergencies. Regular drills and exercises help validate the effectiveness of the BCP and assure readiness to respond to various scenarios.

Steps to Create a Business Continuity Plan
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you develop an IT BCP:
1. Conduct a Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Begin by pinpointing vital business operations, IT systems and dependencies. Evaluate the possible impact of disruptions on these areas and prioritize them based on their importance to your organization’s operations.
2. Identify Risks and Threats
Assess the possible risks and threats that could disrupt your business, including cyberattacks, natural disasters and human error. Consider internal and external factors that could impact your IT infrastructure and operations.
3. Develop Recovery Objectives
Define your organization’s recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs). Determine the maximum acceptable downtime for critical systems and the maximum allowable data loss.
4. Create a Response Plan
Develop a comprehensive response plan outlining the steps to be taken in the event of a disruption. Assign responsibilities to key personnel, establish communication protocols and identify backup systems and alternative work arrangements.
5. Implement Risk Mitigation Measures
Implement measures to mitigate identified risks and threats, such as cybersecurity protocols, backup power systems and off-site data storage facilities.
6. Test and Refine the Plan
Regularly test your IT BCP through simulations and exercises to identify weaknesses and areas for improvement. Update the plan based on test results and changes in your organization’s operations or IT infrastructure.
7. Train Employees
Ensure all employees are trained properly. Conduct regular training sessions and drills to familiarize employees with the IT BCP and confirm they know how to respond effectively.
Business Continuity Plan Implementation
Here’s how to effectively put your IT BCP into action:
- Assign responsibility: Designate individuals or teams responsible for overseeing the implementation of the BCP. Clearly outline their roles and responsibilities to ensure accountability.
- Communicate the plan: Make sure all employees are aware of the BCP and understand their roles during a crisis. Conduct training sessions and provide regular updates to keep everyone informed.
- Activate the plan: When a disruption occurs, activate the BCP according to predefined triggers and protocols. Follow the established procedures for responding to the specific type of incident.
- Coordinate response: Collaborate with key stakeholders and departments to execute the BCP effectively. Maintain open lines of communication and ensure everyone is working toward the common goal of minimizing downtime and restoring operations.
- Monitor progress: Continuously monitor the implementation of the BCP to track progress and identify any issues or gaps. Make adjustments as necessary to ensure the plan remains effective.
- Review and learn: After the crisis has passed, conduct a thorough review of the BCP implementation process. Identify lessons learned and areas for improvement to enhance future responses.
Business Continuity Plan Testing
Testing your IT BCP helps you make sure it’s effective in real-world scenarios. Here are key steps to conduct thorough BCP testing:
- Identify testing scenarios: Determine various scenarios that could disrupt business operations, such as cyberattacks, natural disasters or equipment failures.
- Define testing objectives: Clearly outline the goals and objectives of the testing process. This includes assessing the plan’s ability to minimize downtime, restore critical systems and maintain essential functions.
- Select testing methods: Choose appropriate testing methods based on your organization’s resources and capabilities. Options include tabletop exercises, simulations, walk-throughs and full-scale drills.
- Involve key stakeholders: Engage stakeholders from different departments and levels of the organization in the testing process. This ensures comprehensive evaluation and buy-in from all parties.
- Evaluate results: Assess the testing exercises’ outcomes to identify strengths, weaknesses and areas for improvement. Use feedback to refine the BCP and enhance its effectiveness.
- Iterate and improve: Continuously refine and update the BCP based on lessons learned from testing. Regularly revisit and adjust the plan to address evolving threats and changes in the business environment.
Business Continuity in the Cloud
Cloud technology began gaining traction when businesses started to realize its value, as the cloud’s infrastructure is not at all hardware dependent. This technology enables companies to easily back up applications, data, and even entire operating systems to the cloud. Additionally, the cloud is a completely remote storage place, meaning that it can be accessed at any time and anywhere by any authorized users. There is also an extra layer of security when you use the cloud, as it is completely virtual. Data on physical hardware, on the other hand, can become compromised should the hardware break down or go down. The cloud ensures that regardless of what curve balls are thrown your way, you can rely on it to save your important company data.

Secure Backup Solutions for Business Continuity at Contigo Technology
Leveraging cloud technology for your business continuity and risk management plans is not just a good idea — it is also a way for businesses to take advantage of more security, scalability and reliability regarding data backups and storage.
As a seasoned managed IT support company, we work with our clients to find a data recovery solution that works best for their enterprise. Our goal is to give you a viable plan B so that your data is there when you need it most. Learn more about Contigo’s best-in-class customizable backup solutions.
Learn More About Our Managed Security Solutions